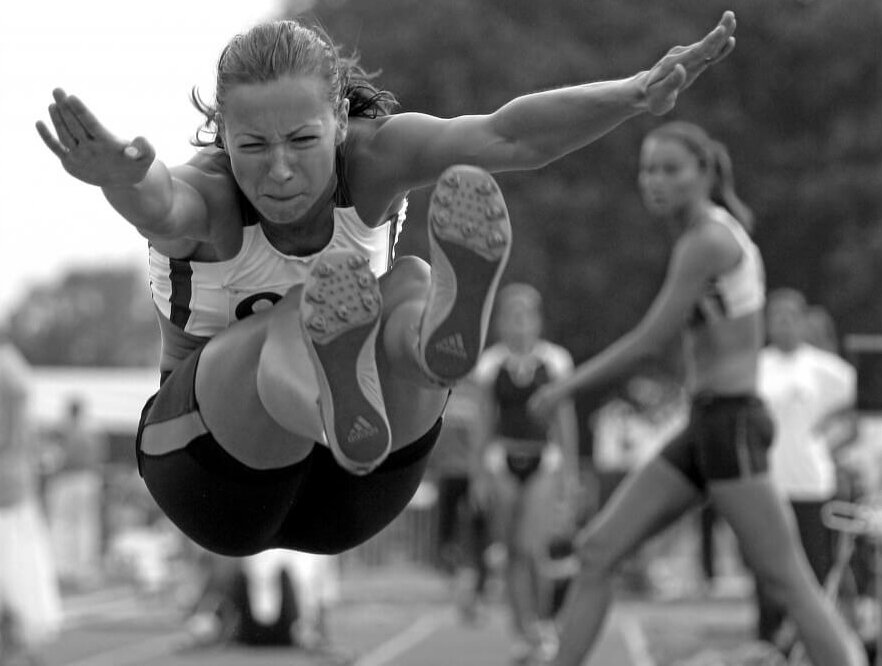
Sport is captivating. Engaging in it elicits strong emotions for many people, like passion, excitement, and love. Sport is so central to many people’s lives that it impacts choices participants and spectators make about how they live. For example, practice and game schedules often determine how one’s days, weeks, and even vacations are planned. In addition, great value is placed on the role of sport in our lives. Sport is argued to be a place where people can learn and practice socially valued behaviors like teamwork, perseverance, and hard work; all characteristics also used to describe valued employees and community members. However, sport can also encourage behaviors that can be negative and damaging. For example, the culture of power and performance sports encourages athletes to play through pain and injury. Those who make that choice are often rewarded through adulation which reinforces their decision. Certain behaviors, including playing through injury, striving for distinction, accepting no obstacles in the pursuit of success, and always putting the game first, combine to create the Sport Ethic, a phenomenon that supports and reaffirms one’s identity as an athlete (Coakley, 2021).

The elements of the Sport Ethic may read to some like a roadmap to building the perfect athlete. Subscribers to the phenomenon may well be aggressive, obedient, and fiercely committed to the team and sport, perhaps to a fault. “They will have to drag me off the field.” “All I want is all you got.” “Softball is life.” “Leave it all on the field.” These and similar statements are common affirmations of the Sport Ethic with each communicating that we, as coaches and parents, expect student-athletes to place the game before their well-being, relationships with others, and their future. That is really the core of the Sport Ethic; interrelated behaviors and ways of thinking exhibited in our actions and communications that encourage one to put the sport first. However, overuse injuries and dysfunctional work and personal relationships are potential consequences to the adoption of and over-conformity to the Sport Ethic, where the risk of serious injury is predictable in those who ignore minor injuries (Coakley, 2021).